La chute des cheveux représente pour beaucoup de personnes un préjudice esthétique considérable. Parmi les nombreuses causes possibles, l’alopécie androgénique est de loin la plus fréquente puisqu’elle touche 50% des hommes et 25% des femmes.
Origine de l’alopécie androgénique
L’alopécie androgénique correspond à une chute progressive des cheveux d’origine héréditaire et hormonale. Il y a donc 2 aspects dans l’origine de cette alopécie :
- ANDRO = la chute des cheveux provient d’une réaction anormale des cheveux aux androgènes (hormones mâles qui sont présentes aussi chez la femme).
- GENIQUE = cette réaction anormale est liée à une prédisposition génétique.
En résumé, on peut dire que l’alopécie androgénique est une trop grande sensibilité aux hormones mâles due à l’hérédité.
On a longtemps cru que l’alopécie androgénique était liée à une surproduction de testostérone. C’est pourquoi on attribuait aux chauves une virilité au-dessus de la moyenne.
On sait actuellement que c’est faux : ce n’est pas une production de testostérone supérieure à la moyenne mais plutôt une sensibilité accrue des follicules pileux aux hormones mâles.
Cette pathologie n’est donc pas un trouble hormonal mais un fonctionnement anormal au niveau de la peau du cuir chevelu.
La testostérone se transforme sous l’influence d’une enzyme, la 5α –réductase, en dihydrotestostérone (DHT) qui va stimuler les glandes sébacées. Celles-ci augmentent leur production de sébum qui va stagner dans le follicule pileux et l’obstruer progressivement. Le cuir chevelu s’épaissit et empêche les vaisseaux sanguins de bien nourrir le bulbe.
Une autre action négative de la DHT, c’est qu’elle raccourcit la période du cycle vital du cheveu qui est d’environ 4 ans pour un homme.
Stimulé par l’hormone mâle, le cycle vital du cheveu ne dure plus qu’un à deux ans.
Ces 2 phénomènes conjugués feront que les cheveux affaiblis tombent avant d’avoir atteint leur longueur maximale et cèdent leur place à des nouvelles repousses qui auront aussi une durée de vie raccourcie. Les 15 ou 20 cycles pilaires prévus pour une vie entière seront épuisés beaucoup plus rapidement, en 15 à 20 ans environ au lieu de 40 à 50 ans, sans qu’il soit possible au cuir chevelu de créer de nouveaux bulbes. Tout cela explique pourquoi chaque nouveau cheveu sera toujours plus fin et plus court que le précédent avec une évolution progressive vers un duvet puis enfin vers la calvitie.
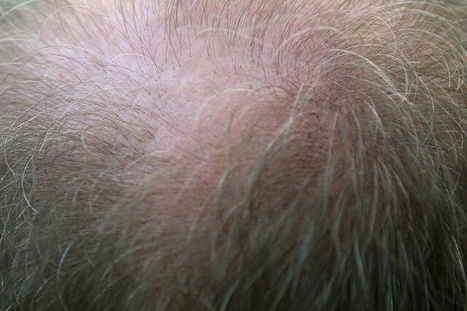
Alopécie androgénique chez la femme
Elle est moins fréquente et moins marquée que chez l’homme et ne se termine jamais en calvitie totale. Les femmes peuvent présenter une alopécie androgénique à tout âge mais surtout autour ou après la ménopause.
Chez la femme, la chute des cheveux commence par un élargissement de la raie au sommet du crâne car les cheveux deviennent plus fins et moins nombreux. Ainsi, la femme ne présente pas de plaques chauves, elle constate plutôt un dégarnissement du sommet de sa tête.
Traitement de l’alopécie androgénique
Les traitements classiques
- Le Minoxidil (Alopexy, Alostil, Regaine)
C’est un ancien médicament hypotenseur dont les effets secondaires étaient le développement de cheveux inopinés sur les tempes. Appliqué localement, il prolonge la vie du cheveu malade, lui permettant d’augmenter son volume et sa longueur. Il n’y a donc pas d’augmentation du nombre de cheveux mais plutôt de leur volume. Il faut six mois pour voir des résultats généralement peu spectaculaires. Les effets secondaires sont des palpitations, de l’hypotension et de l’irritation du cuir chevelu. - Le Finastéride ( Propecia)
Le traitement ne fonctionne que dans 48% des cas et les effets secondaires sont impuissance et troubles de la libido.
Les produits Follon : une révolution en cosmétologie médicale
On sait que c’est les hormones mâles (dans les 2 sexes) qui sont à l’origine du développement de l’alopécie androgénique selon la séquence suivante :
production de sébum ► Testostérone ► 5α –réductase ► DHT ► diminution cycle vital ► ALOPECIE
C’est pourquoi des chercheurs ont imaginé pouvoir contrôler la production de ces hormones mais uniquement au niveau local (la peau). La solution est de trouver une substance capable de bloquer l’action de l’enzyme 5α –réductase.
Après plusieurs années de recherches et beaucoup d’expériences de laboratoire, ils ont conclu qu’un complexe de phytostérols avec du β-sitostérol comme substance primaire pourrait devenir un agent très actif et en même temps complètement inoffensif pour l’inhibition des hormones sexuelles localement au niveau de la peau.
L’innovation de cette nouvelle philosophie se situe dans le fait que, pour la première fois, l’inhibition de l’activité enzymatique se fait exclusivement localement sans interférence systémique et par conséquent, avec absolument aucun effet indésirable.
Cette méthode d’inhibition locale des hormones stéroïdes sexuelles fait l’objet d’un brevet international (Patent No.PCT/EP00/07315)
Le complexe de phytostérols va agir en bloquant l’activité de l’enzymze 5α –réductase au niveau du cuir chevelu. Cela aura pour conséquence une diminution de la conversion de la testostérone en DHT et donc une amélioration spectaculaire de l’alopécie androgénique.
Follon Teinture
La teinture Follon est un traitement local pour l’alopécie androgénetique qui incorpore l’innovation médicale de l’inhibition locale des hormones sexuelles grâce aux phytostérols brevetés. On y retrouve également du. Sabal serrulata (inhibiteur de la DHT), du tussilage (anti-inflammatoire local), de la mauve (plante antiseptique pour la prévention des infections locales), du rétinol (Vitamine A pour la réparation des cheveux), de la biotine (pour la croissance du cheveu) et du Zinc (rôle anti-séborrhéique)
Mode d’utilisation :
Faire 6 à 10 pulvérisations 2x/jour (matin et soir) sur des cheveux et un cuir chevelu propre (non gras). Les cheveux pourront être secs ou mouillés. Masser légèrement le produit sur le cuir chevelu. Chez les personnes très dégarnies, on recommande de pulvériser la teinture surtout sur la frontière entre les cheveux existants et la partie dégarnie.
Follon Gélules
Il contient également le complexe de phytostérols et de l’extrait d’urtica dioica toujours pour bloquer l’action locale de la DHT. Le fenugrec qui améliore fortement la microcirculation au niveau de la racine du cheveu. L’acide folique et pantothénique, les Vitamines B2 et B6 sont des adjuvants classiques utilisés pour favoriser la croissance des cheveux.
Mode d’utilisation :
2 gélules par jour à distance des repas (30 min. avant ou 1h.30 après).



